Table of Contents
- Understanding Storage Scalability
- Assessing Your Storage Requirements
- Implementing Scalable Storage Solutions
- Leveraging Predictive Analytics
- Automating Storage Management
- Considering Edge Computing
- Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
- Conclusion
Business expansion increases data demands, making it essential for organizations to adopt adaptable, robust storage strategies. Without adequate storage scalability, companies may encounter performance bottlenecks, data loss risks, and spiraling costs. Learning about solutions like RAID 10 and modern data architectures can equip organizations to manage and accelerate their growth securely and efficiently.
Implementing scalable storage isn’t just about capacity; it’s about ensuring rapid data access, guaranteeing compliance, and safeguarding sensitive information. Whether your company manages customer records, supports real-time analytics, or delivers multimedia experiences, your ability to dynamically scale storage directly impacts business performance, customer satisfaction, and operational agility.
Knowing how different scaling methods work, when to deploy each, and the unique considerations that go into the decision-making process ensures you can proactively solve storage challenges rather than react to crises. This approach allows your business to pursue opportunities without being held back by technical limitations. Adopting the right mix of hardware, cloud integrations, and analytics will put your company in a position for long-term success, with the agility to shift resources as markets and demands evolve.
Understanding Storage Scalability
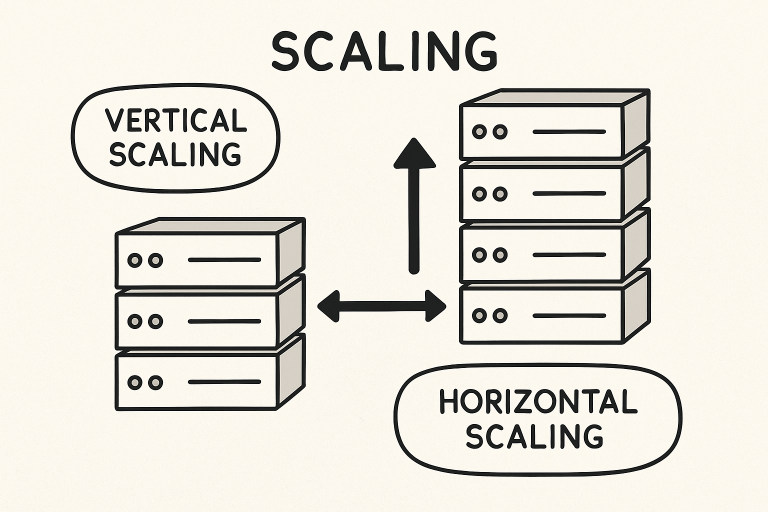
Storage scalability refers to a system’s ability to effectively manage increasing data volumes and performance requirements. It can be achieved through two main methods: vertical scaling (scale-up) and horizontal scaling (scale-out). Vertical scaling enhances the existing hardware’s capacity by upgrading components such as memory or storage drives within a server. Conversely, horizontal scaling adds more servers or nodes in a distributed network to boost performance and provide redundancy. The choice between these strategies depends on factors such as budget, technical requirements, and the current system architecture. Organizations that require quick adaptability to workload fluctuations often prefer horizontal scaling due to its inherent flexibility and fault tolerance.
In addition, storage scalability is crucial for supporting modern applications that generate large amounts of unstructured data, such as video, IoT, and analytics workloads. Cloud environments often use horizontal scaling to dynamically distribute storage across multiple regions, improving both availability and resilience. Efficient scalability also helps optimize costs by allowing organizations to add resources incrementally rather than over-provisioning upfront. Ultimately, a well-planned storage scalability strategy ensures that systems can grow seamlessly with business demands while maintaining performance and reliability.
Assessing Your Storage Requirements
An accurate assessment of storage needs is essential for an effective scaling strategy, starting with an analysis of historical data growth trends and future predictions. It is important to identify business-critical data, understand retrieval speed requirements, and recognize which data can be stored using lower-cost infrastructure. Key components of this assessment include tracking data growth rates across data creation, use, and archiving to predict fluctuations; segmenting applications based on performance needs, such as latency and throughput, for mission-critical databases versus archived records; and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Incorporating continuous reassessment into the IT planning cycle helps optimize resource allocation by preventing over-provisioning, which wastes costs, and under-provisioning, which risks outages and performance bottlenecks.
Implementing Scalable Storage Solutions
Organizations can utilize various scalable storage architectures such as Cloud Storage, Software-Defined Storage (SDS), and Hybrid Storage. Cloud Storage provides resource elasticity with easy pay-as-you-go scaling and requires minimal investment in on-premises hardware. SDS separates storage services from the underlying hardware, enabling centralized management across hybrid environments. Hybrid Storage merges in-house control with cloud agility, balancing performance and cost. For example, businesses facing unpredictable data growth can quickly increase capacity using cloud storage and often combine it with SDS for efficient automation and resource management across both cloud and physical infrastructures.
Leveraging Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics employs historical and real-time data to forecast when and what type of storage expansion is necessary. By analyzing trends in file sizes, access patterns, and workloads, companies can avoid unnecessary hardware costs and ensure they’re not caught off guard by usage spikes. For example, media production firms routinely utilize predictive analytics tools to automatically reallocate resources during large video renders, avoiding both underutilization and sudden slowdowns.
Automating Storage Management
Automation, enabled by intelligent software and orchestration tools, automatically provisions or decommissions storage resources as required. Automated scaling tools can react to peak loads by bringing additional disks or virtual instances online, then scale back during off-hours, significantly reducing manual oversight and operational costs. E-commerce businesses, for example, depend on this technology to remain agile during events like holiday sales, when transaction volumes can surge unpredictably.
Considering Edge Computing
Edge computing, which brings processing and storage closer to the data source, plays a critical role in industries that rely on real-time analytics or remote operations, such as manufacturing, logistics, and oil and gas. By minimizing the distance data travels, edge nodes reduce latency and bandwidth consumption. A global logistics firm, for example, might deploy edge devices at distribution centers to instantly update shipment statuses and inventory counts, improving both accuracy and response time.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
As infrastructure scales, security and regulatory demands multiply. It’s critical to implement best-in-class encryption, role-based access controls, and regular security reviews. Additionally, storage solutions should natively support industry and geographic compliance standards, such as PCI DSS for payment card data or HIPAA for health information. Failure to meet these standards can result in penalties and severe reputational harm, so prioritizing robust safeguards must go hand in hand with any scaling initiative.
Conclusion
Efficient, strategic storage scalability is the foundation of modern business agility and resilience. By accurately sizing storage now and planning for tomorrow’s growth using scalable architectures, predictive analytics, automation, and robust security, companies can meet their business needs head-on, no matter how much data their future holds.



